A responsive navigation bar is a core component of any modern website.
In this tutorial, we build a fully responsive navbar using only HTML & CSS, without using JavaScript. This approach keeps the navbar lightweight, fast, and easy to maintain.
This project is beginner-friendly and ideal for developers who want to understand CSS layouts, media queries, and responsive design principles.
Tools & Resources That Support My Web Development Work
Discover the exact hardware and services I use daily — from laptops and keyboards to hosting and domains.
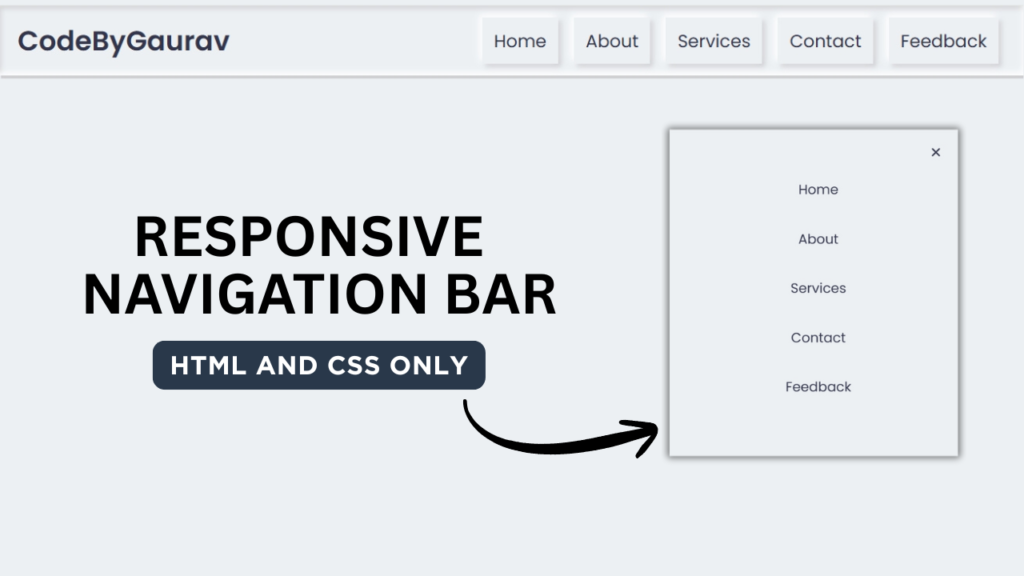
1. Video Tutorial – Responsive Navbar (HTML & CSS)
Watch the complete step-by-step video tutorial to see how the responsive navbar is created and how it adapts to different screen sizes.
The video covers:
Desktop navbar layout
Mobile toggle behavior (CSS-only)
Responsive breakpoints
2. HTML Structure of the Navbar
The HTML part defines the structure of the navigation bar, including:
Logo / brand name
Navigation links
Mobile menu toggle elements
Below is the complete HTML code used for this responsive navbar.
👉 Full HTML Code Below
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Responsive Navbar | CodeByGaurav</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/font-awesome/7.0.1/css/all.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<nav>
<div class="menu">
<input type="checkbox" id="check">
<div class="logo"><a href="#">CodeByGaurav</a></div>
<ul>
<label class="btn cancel" for="check">
<i class="fa-solid fa-xmark"></i>
</label>
<li><a href="#">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="#">About</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Services</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Contact</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Feedback</a></li>
</ul>
<label class="btn bars" for="check"><i class="fa-solid fa-bars"></i></label>
</div>
</nav>
</body>
</html>
3. CSS Styling & Responsiveness
CSS handles the entire responsiveness of the navbar:
Desktop layout styling
Mobile menu visibility
Smooth transitions and spacing
Responsive breakpoints
With proper CSS structure, the navbar adapts smoothly across devices.
👉 Full CSS Code Below
@import url("https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Poppins:ital,wght@0,100;0,200;0,300;0,400;0,500;0,600;0,700;0,800;0,900;1,100;1,200;1,300;1,400;1,500;1,600;1,700;1,800;1,900&display=swap");
* {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-family: "Poppins", sans-serif;
}
body{
background: #ecf0f3;
}
nav{
width: 100%;
padding: 12px 0;
background: #ecf0f3;
box-shadow: -3px -3px #ffffff, 3px 3px #ceced1, inset -3px -3px 7px #ffffff, inset 3px 3px 5px #ceced1;
}
nav .menu{
max-width: 1270px;
margin: auto;
padding: 0 20px;
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
}
.menu .logo a{
font-size: 28px;
font-weight: 600;
text-decoration: none;
color: #31344b;
}
.menu ul{
list-style: none;
display: flex;
}
.menu ul a{
margin: 0 8px;
text-decoration: none;
font-size: 18px;
color: #31344b;
font-weight: 400;
display: inline-block;
padding: 10px 12px;
box-shadow: -3px -3px 7px #ffffff, 3px 3px 5px #ceced1;
position: relative;
transition: all 0.3s ease;
}
.menu ul a:hover::before{
content: "";
position: absolute;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
box-shadow: inset -3px -3px 7px #ffffff, inset 3px 3px 5px #ceced1;
}
.menu ul a:hover{
color: #3498db;
}
nav label.btn{
color: #31344b;
font-size: 18px;
cursor: pointer;
display: none;
}
nav label.cancel{
position: absolute;
top: 25px;
right: 30px;
}
#check{
display: none;
}
@media (max-width:940px){
.menu ul{
display: block;
position: fixed;
top: 0;
left: -100%;
width: 100%;
min-width: 400px;
padding-top: 45px;
height: 100%;
background: #ecf0f3;
box-shadow: 0 5px 10px #b0b0b5;
z-index: 12;
transition: all 0.3s ease;
}
.menu ul a{
display: block;
font-size: 23px;
width: 100%;
margin-top: 30px;
box-shadow: none;
text-align: center;
}
.menu ul a:hover::before{
box-shadow: none;
}
nav label.bars{
display: block;
}
#check:checked~label.bars{
display: none;
}
#check:checked~ul label.cancel{
display: block;
}
#check:checked~ul{
left: 0;
}
}
4. Why Build a Navbar Without JavaScript?
Using only HTML & CSS helps to:
Improve website performance
Reduce complexity
Avoid unnecessary scripts
Create beginner-friendly solutions
Enhance accessibility and maintainability
This approach is perfect for static websites, portfolios, and landing pages.
Final Conclusion
A Responsive Navbar using Only HTML & CSS is a practical and valuable frontend project.
It strengthens your understanding of responsive layouts and modern CSS techniques without relying on JavaScript.
This project is highly recommended for beginners who want to build clean, efficient, and professional website components.